Understanding Gynecological Health: Essential Insights for Women
Introduction to Gynecological Health: Gynecological health encompasses a vast spectrum of issues relevant to women’s reproductive systems, playing a crucial role in their overall well-being. This field of healthcare primarily concerns the health of the female reproductive organs, including the uterus, ovaries, and vagina. Women experience various significant phases throughout their lives, including menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, all of which are integral components of Gynecological health.
Menstruation is often the first aspect of Gynecological health that women encounter. Understanding the menstrual cycle is essential, as it provides insight into a woman’s reproductive health and can highlight underlying health issues. Regular cycles typically indicate a well-functioning reproductive system, while irregularities may signal hormonal imbalances or other health problems that warrant professional attention.
Pregnancy is another critical period that underscores the importance of Gynecological health. Ensuring optimal reproductive health before, during, and after pregnancy is pivotal for both the mother and the baby. Prenatal care, which includes regular check-ups and screenings, helps monitor the health of both parties and can prevent complications during childbirth. Expectant mothers need to have access to accurate information and support during this transformative stage of life.
On the other hand, menopause marks a significant transition in a woman’s life, typically occurring in their late 40s to early 50s. This stage can come with symptoms such as hot flashes, mood changes, and sleep disturbances, making it vital for women to seek guidance from healthcare professionals. Understanding these changes and their implications is crucial in managing one’s health effectively.
Overall, regular check-ups and being attuned to one’s own body significantly contribute to a better understanding of Gynecological health. Engaging in preventive care not only helps in the early detection of potential issues but also promotes a proactive approach to women’s health throughout their lives.

Common Gynecological Conditions
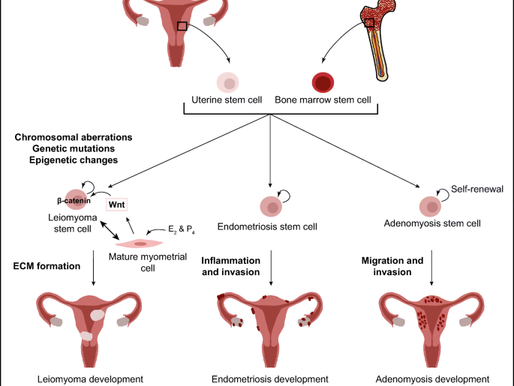
Common Gynecological Conditions: Gynecological health is a crucial aspect of women’s overall well-being, encompassing various conditions that can significantly impact their quality of life. One common condition is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), a hormonal disorder characterized by irregular menstrual cycles, excess androgen levels, and polycystic ovaries. Women with PCOS may experience symptoms such as weight gain, acne, and hair loss. The exact cause of PCOS remains unclear, but it is often linked to insulin resistance and genetic factors, which can result in complications such as infertility and an increased risk of metabolic syndrome.
Another prevalent condition is endometriosis, where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, often causing significant pain and discomfort. Symptoms may include severe menstrual cramps, chronic pelvic pain, and pain during intercourse. Endometriosis can impact fertility and is linked to the development of ovarian cysts. Awareness and early diagnosis are essential to manage this condition effectively, as treatment options may include pain management and, in severe cases, surgery.
Uterine fibroids, benign tumors that develop in the uterus, are also common among women of reproductive age. They can lead to symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and pressure symptoms. While the precise cause of fibroids is unknown, hormonal factors play a significant role in their development. In many instances, fibroids do not require treatment, but when they do, options may range from medication to surgical intervention, depending on the severity of symptoms.
Infections such as bacterial vaginosis, yeast infections, and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are additional concerns in Gynecological health. Symptoms can vary widely, including itching, unusual discharge, and pain during urination. Prompt medical attention is crucial for diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications. Understanding these common Gynecological conditions can empower women to seek appropriate care, enhancing their health and quality of life.
Importance of Regular Gynecological Exams
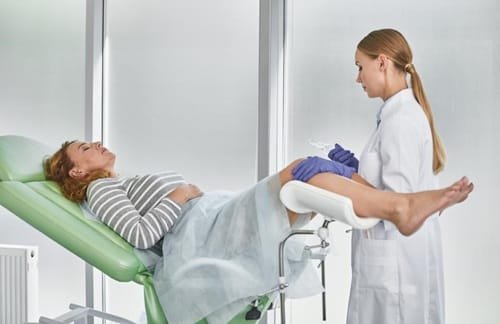
Importance of Regular Gynecological Exams: Routine Gynecological exams are essential for maintaining women’s health and play a critical role in the early detection and prevention of various health conditions. These exams typically include Pap smears and pelvic examinations, which are designed to assess reproductive health, identify potential issues, and provide women with vital information about their bodies. Engaging in regular Gynecological check-ups fosters a proactive approach to health, empowering women to make informed decisions and promote their overall well-being.
Pap smears are particularly significant as they help in the early detection of cervical cancer and pre-cancerous changes. The frequency of Pap smears generally depends on a woman’s age and health history. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends that women begin screening at age 21 and continue every three years until the age of 29. Women aged 30 to 65 may opt for a Pap smear every three years or a combination of Pap smear and HPV (human papillomavirus) testing every five years, depending on their risk factors.
Pelvic exams, on the other hand, assess the overall health of the reproductive organs and can help identify conditions such as fibroids, ovarian cysts, or infections. These exams are usually conducted annually, beginning at the onset of sexual activity or around the age of 21. During a typical visit, women can expect a discussion about their medical history, any concerns they may have, and a physical examination that may include a breast exam as well.
Incorporating regular Gynecological exams into one’s healthcare routine not only aids in addressing existing health issues but also serves as a preventative measure against their future occurrence. By prioritizing these exams, women can enhance their Gynecological health and ensure they remain informed about their reproductive wellbeing.
Understanding Menstrual Health
Understanding Menstrual Health: Menstrual health is a vital aspect of Gynecological well-being, encompassing the regularity and nature of menstrual cycles, common disorders, and management strategies for menstrual discomfort. A typical menstrual cycle lasts between 21 to 35 days, with bleeding lasting approximately three to seven days. Variations in cycle length, flow intensity, and associated symptoms can be normal; however, significant changes may indicate underlying health issues.
Common menstrual disorders include dysmenorrhea, or painful menstruation, and amenorrhea, which is the absence of menstruation. Dysmenorrhea can range from mild cramps to severe pain that disrupts daily activities, often caused by uterine contractions during menstruation. The management of this pain can involve a range of options from over-the-counter pain relief medications to lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, dietary changes, and stress reduction techniques. Women experiencing consistent pain or discomfort should consult healthcare providers for personalized treatment options.
Another significant aspect of menstrual health is the influence of lifestyle factors. Diet, physical activity, stress levels, and overall health can all affect menstruation. For instance, a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports hormonal balance and may alleviate some menstrual symptoms. Conversely, excessive exercise or extreme weight changes can lead to irregular cycles or amenorrhea. Additionally, stress management techniques, including mindfulness and relaxation exercises, can contribute positively to hormonal health.
Women need to be aware of their menstrual health and recognize when to seek medical advice. Signs that may warrant a consultation include excessively heavy bleeding, cycles shorter than 21 days, or severe pain that is not alleviated by standard pain relief. Understanding and monitoring menstrual health empowers women to advocate for their well-being and seek appropriate intervention when necessary.
Mental Health and Gynecological Issues
Mental Health and Gynecological Issues: The interplay between gynecological health and mental well-being is significant and often underappreciated. Women experiencing gynecological issues such as premenstrual syndrome (PMS), endometriosis, and menopause frequently report heightened levels of emotional distress. PMS, for example, is known to cause not only physical symptoms like bloating and cramps but also mood swings, anxiety, and depression. These psychological symptoms can severely impact an individual’s quality of life, making it crucial to address both aspects of this condition.
Endometriosis, a condition where tissue similar to the lining inside the uterus grows outside of it, poses another challenge. Besides the debilitating pain and complications related to fertility, studies have shown that women with endometriosis often experience anxiety and depression at higher rates compared to those without the condition. This correlation highlights the need for integrated care, as physical treatments alone may not suffice to alleviate the emotional burdens associated with endometriosis.
Menopause, a natural phase in a woman’s life, can also lead to significant psychological changes. The hormonal fluctuations that occur during this time can contribute to mood swings, irritability, and feelings of sadness or hopelessness. Women might find themselves grappling with feelings of loss or identity changes, which can intensify mental health concerns. The emotional implications of menopause are, therefore, essential discussions in gynecological health care.
Given these connections, healthcare providers must adopt a holistic approach to treating gynecological issues. By integrating mental health support within the treatment of physical conditions, women can achieve better overall wellness. Addressing psychological aspects while managing gynecological health leads to more effective outcomes, empowering women to lead healthier and more fulfilling lives.

Hormonal Health and Reproductive Well-being
Hormones play a pivotal role in Gynecological health, intricately influencing various aspects of the reproductive system. They regulate a multitude of bodily functions, including the menstrual cycle, ovulation, and pregnancy. An imbalance in hormones can lead to a range of reproductive health issues, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, infertility, and irregular menstrual cycles. Understanding these hormonal fluctuations is essential for women to navigate their reproductive health effectively.
Hormonal imbalances can arise from various factors including stress, poor diet, lack of exercise, and environmental toxins. For instance, elevated levels of cortisol, a stress hormone, can disrupt the delicate interplay of reproductive hormones, leading to complications such as missed periods or difficulties in conceiving. Women must recognize the signs of hormonal imbalance, which may manifest as mood swings, weight changes, fatigue, or disruptions in their menstrual cycle.
Managing hormonal health effectively requires a multifaceted approach. Lifestyle changes are often the first line of defense. Incorporating a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, maintaining a healthy weight, and regular physical activity can significantly influence hormonal balance. Additionally, stress management techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises can alleviate some of the negative impacts of stress on hormonal health.
In some cases, medical interventions may be necessary. Hormonal therapies including birth control pills, hormone replacement therapy, or medications to address specific conditions such as PCOS can be prescribed. Women need to consult with healthcare professionals to determine the most appropriate treatment options tailored to their individual needs. Overall, understanding the role of hormones in Gynecological health empowers women to take proactive steps in managing their reproductive well-being.

Sexual Health and Education
Sexual health education plays a crucial role in empowering women to take control of their bodies and make informed decisions regarding their sexual well-being. Comprehensive sexual health education provides essential information about safe sex practices, consent, and the intricacies of one’s own anatomy. Recognizing that sexual health is an integral part of overall Gynecological health is vital, as it influences physical, emotional, and social well-being.
To begin with, understanding safe sex practices is essential for preventing sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and unplanned pregnancies. Women should be educated on the various methods of protection available, such as condoms and dental dams, and how to correctly use them. It is also important to discuss the significance of regular STI screenings and routine health check-ups, as these proactive measures can significantly enhance one’s sexual health.
Consent is a crucial element of sexual health that must be clearly understood. Education about consent ensures that individuals appreciate the necessity of mutual agreement in sexual activities. This understanding empowers women to establish boundaries, communicate their desires, and foster respectful and safe interactions. Teaching about consent also contributes to dismantling harmful attitudes surrounding sexual relationships, promoting a culture where autonomy and respect prevail.
Furthermore, self-exploration and understanding one’s own body are fundamental aspects of sexual health education. Women are encouraged to familiarize themselves with their anatomy and menstrual cycles, which can help them recognize what is normal versus abnormal regarding their Gynecological health. This knowledge assists them in identifying any concerning symptoms that may require medical attention.
For further education, numerous resources are available, including workshops, online courses, and informative websites dedicated to sexual health and Gynecological knowledge. Engaging with these resources can enhance understanding and foster a healthier relationship with one’s sexual health, ultimately contributing to overall well-being.

Pregnancy and Gynecological Care
Gynecological care is an essential component of healthcare for women, especially during pregnancy. The prenatal phase is a critical period that requires comprehensive medical attention to ensure the health and safety of both the mother and the developing fetus. Regular Gynecological check-ups throughout pregnancy empower healthcare providers to monitor the progress of the pregnancy, address any complications, and provide necessary resources for expectant mothers.
One of the primary aspects of prenatal care involves routine visits to a gynecologist or obstetrician. During these visits, healthcare professionals assess vital parameters such as maternal weight, blood pressure, and fetal heartbeat. These assessments not only help track the progression of the pregnancy but also enable early detection and management of potential complications, such as gestational diabetes or hypertension.
Moreover, common concerns arise during pregnancy that necessitate informed Gynecological support. Symptoms such as morning sickness, fatigue, or unusual discomfort may lead women to seek professional guidance. A qualified gynecologist can offer recommendations to alleviate these symptoms while ensuring they do not pose risks to maternal or fetal health. Furthermore, proper Gynecological care fosters discussions around nutrition, exercise, and mental well-being, equipping expectant mothers with resources to maintain a healthy lifestyle during this transformative time.
Coverage of various screening tests is another benefit of Gynecological care during pregnancy. Conditions such as chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus can be assessed through non-invasive prenatal testing. The insights gained through Gynecological evaluations allow parents to make informed decisions regarding their pregnancy and prepare adequately for delivery. Through consistent Gynecological care, mothers gain ongoing support and the ability to navigate the many changes that accompany pregnancy while prioritizing the health of their child.

Menopause: What to Expect
Menopause is a natural biological process marking the end of a woman’s reproductive years, typically occurring between the ages of 45 and 55. It is defined as the point when a woman has not menstruated for 12 consecutive months, signaling a decline in estrogen and progesterone production by the ovaries. This transition can be categorized into three distinct stages: perimenopause, menopause, and postmenopause. During perimenopause, which may last several years, women may begin to experience irregular menstrual cycles along with various symptoms as hormone levels fluctuate.
Common symptoms associated with menopause include hot flashes, night sweats, mood changes, sleep disturbances, and vaginal dryness. These symptoms can greatly impact a woman’s quality of life, prompting many to seek management strategies. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is a common option, as it can help alleviate symptoms by restoring hormonal balance. However, women need to consult healthcare professionals to discuss the risks and benefits, as HRT may not be suitable for everyone.
In addition to HRT, lifestyle adjustments play a pivotal role in managing menopausal symptoms. Regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight, improve mood, and reduce the frequency of hot flashes. A balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is crucial for bone health, as menopause increases the risk of osteoporosis. Staying hydrated and incorporating mindfulness techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can also assist in managing stress and promoting overall well-being.
The long-term implications of menopause on women’s health should not be overlooked. Increased risks of cardiovascular disease and osteoporosis underscore the importance of proactive health management. Regular health check-ups and open discussions with healthcare providers can help women navigate this significant life transition, ensuring they maintain a favorable quality of life during and after menopause.
If you like our posts about Gynecological Health, Common Gynecological Conditions, Importance of Regular Gynecological Exams, Understanding Menstrual Health, Mental Health and Gynecological Issues, etc, then follow us on Facebook, Instagram, X, and WhatsApp. Thank You.
Read More: Orthopedic Range


