Introduction to Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic
Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic: The field of medical science has long recognized the critical role that anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents play in the management of various conditions associated with pain and inflammation. Understanding the properties and functions of these agents is essential for both healthcare professionals and patients, as they form the foundation of effective therapeutic strategies. Anti-inflammatory agents are primarily used to reduce inflammation, which is the body’s natural response to injury or infection. This response, while vital for healing, can become detrimental when excessive, leading to chronic conditions that require medical intervention.
On the other hand, analgesic agents are specifically designed to alleviate pain, offering relief to individuals suffering from acute or chronic discomfort. Pain management is a complex area of healthcare, and effective analgesia can significantly enhance a patient’s quality of life. These agents function through various mechanisms, including the inhibition of pain-signaling pathways and the modulation of inflammatory responses. As such, both anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties are intertwined, often working in tandem to provide comprehensive relief.
The significance of understanding these properties extends beyond clinical settings; it empowers patients to make informed decisions regarding their treatment options. Knowledge of anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents fosters better communication between patients and healthcare providers, leading to tailored treatment plans that address individual needs. Moreover, as medical research advances, new formulations and therapies continue to emerge, highlighting the dynamic nature of this field.
In essence, anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents are indispensable in modern medicine and crucial for managing pain and controlling inflammation. A deeper comprehension of these agents not only enhances patient care but also supports ongoing advancements in therapeutic approaches, ultimately contributing to improved health outcomes.
Types of Anti-Inflammatory Agents
Types of Anti-Inflammatory Agents: Anti-inflammatory agents play a crucial role in managing inflammation, a physiological response that can contribute to various health issues. The most widely recognized types of anti-inflammatory medications include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and natural remedies.
NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, function by inhibiting enzymes known as cyclooxygenases (COX), which are responsible for the synthesis of prostaglandins. These chemical compounds are associated with the inflammatory response, causing pain and swelling. Commonly used for conditions like arthritis, muscle pain, and headaches, NSAIDs provide both analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. However, potential side effects may include gastrointestinal issues and an increased risk of cardiovascular events, particularly with prolonged use.
Corticosteroids, like prednisone and dexamethasone, mimic the effects of hormones produced by the adrenal glands. They work by suppressing the immune response and reducing inflammation. These agents are beneficial in treating a variety of conditions, including autoimmune diseases and severe allergic reactions. While corticosteroids are effective in managing inflammation, long-term use can lead to significant side effects such as weight gain, osteoporosis, and increased susceptibility to infection.
Natural remedies, such as curcumin (found in turmeric), ginger, and omega-3 fatty acids, have gained popularity as adjunct treatments for inflammation. Curcumin, for instance, has shown promise in clinical studies for its ability to modulate inflammatory pathways. Similarly, omega-3 fatty acids, commonly sourced from fish oil, contribute to reduced levels of inflammatory markers in the body. Although generally considered safe, their efficacy can vary, and potential interactions with conventional medications should be evaluated.
Understanding the different types of anti-inflammatory agents is vital for selecting the appropriate treatment options, considering each agent’s mechanism of action, benefits, and possible side effects.

Types of Analgesic Agents
Types of Analgesic Agents: Analgesic agents play a crucial role in pain management, with various types available to address different types of pain and medical conditions. These agents can be categorized into three primary groups: over-the-counter medications, prescription opioids, and alternative therapies. Each category contains various formulations that possess unique mechanisms of action, efficacy, and risks.
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications are often the first line of defense against mild to moderate pain. These commonly include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and aspirin, as well as acetaminophen. NSAIDs work by inhibiting enzymes involved in the inflammatory process, thus reducing pain and swelling. Acetaminophen, on the other hand, is primarily effective in lowering fever and alleviating pain, though its anti-inflammatory properties are limited. While generally considered safe for short-term use, long-term or excessive consumption of OTC analgesics can lead to gastrointestinal issues, liver damage, or increased risk of cardiovascular events.
Prescription opioids, including morphine, oxycodone, and hydrocodone, are utilized for managing moderate to severe pain, often associated with post-surgical recovery or chronic pain conditions. These drugs function by binding to opioid receptors in the central nervous system, diminishing the perception of pain. Despite their effectiveness, opioids carry a risk of addiction, dependency, and overdose when not used appropriately. Therefore, they should be prescribed judiciously and monitored closely for any signs of misuse.
Lastly, alternative therapies may include acupuncture, physical therapy, or herbal remedies. These non-pharmaceutical options often aim to alleviate pain through holistic approaches. For some individuals, these therapies can offer beneficial effects without the side effects associated with traditional analgesics. However, the scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of many alternative treatments varies widely.
Understanding these different categories of analgesic agents is vital for effective pain management. Each option has its unique benefits and risks, necessitating careful consideration by healthcare providers and patients alike to ensure safe and effective pain relief.

The Mechanism of Action: How They Work
The Mechanism of Action How They Work: Anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents play crucial roles in managing pain and inflammation through various biological mechanisms. These agents operate primarily by inhibiting specific enzymes, modulating neurotransmitters, and influencing the immune response, contributing to their therapeutic efficacy. One of the most prominent classes of anti-inflammatory drugs, Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs), functions by blocking the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes. COX enzymes are responsible for the conversion of arachidonic acid into prostaglandins, substances that mediate inflammation and pain. By inhibiting COX-1 and COX-2, NSAIDs effectively reduce the production of these inflammatory mediators, leading to decreased swelling, pain, and fever.
Analgesic properties are also observed in opioids, which function by interacting with specific receptors in the central nervous system. These receptors, known as opioid receptors, upon binding with endogenous or exogenous opioid substances, modulate the perception of pain by altering neurotransmitter release and inhibiting pain pathways. This complex interaction not only offers pain relief but can also induce feelings of euphoria, thereby complicating their usage given the potential for addiction.
The immune response is another critical pathway through which anti-inflammatory agents exert their effects. These agents can modulate immune cell activity, leading to reduced pro-inflammatory cytokine production and enhanced clearance of inflammatory mediators. For example, corticosteroids function by enhancing the expression of anti-inflammatory proteins while suppressing pro-inflammatory gene expression, thus upholding homeostasis in the body.
Understanding these mechanisms highlights the complexity of anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs and underscores the necessity of continuing research to uncover their multifaceted roles in pain management and inflammation control. Accurate application of this knowledge can lead to more effective and targeted therapeutic strategies.
Common Conditions Treated with Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Agents
Common Conditions Treated with Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Agents: Anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents are widely prescribed for a variety of common conditions, effectively alleviating pain and reducing inflammation. One of the most prevalent conditions treated with these medications is arthritis, which encompasses several types, including rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Patients with arthritis often experience chronic pain and inflammation in their joints, making the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) essential for improving their quality of life. NSAIDs reduce inflammation and pain, enabling patients to engage in daily activities with greater ease.
Another condition frequently managed with anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents is muscle injuries. Sprains, strains, and other soft tissue injuries result in pain and swelling. In such cases, an appropriate regimen involving NSAIDs can help mitigate discomfort while promoting the healing process. Physicians may recommend these medications along with physical therapy for a comprehensive recovery approach.
Additionally, migraines are a common ailment that often necessitates the use of analgesics for relief. Patients suffering from acute migraine attacks may benefit from over-the-counter or prescription-strength analgesics, such as acetaminophen or specific NSAIDs. These medications help alleviate intense pain, making it crucial for effective migraine management.
Chronic pain syndromes, such as fibromyalgia and chronic back pain, also see significant treatment involvement from anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents. Patients with such conditions may require a multidisciplinary treatment plan that includes medication, physical therapy, and sometimes cognitive behavioral therapies to address both physical discomfort and the psychological impact of chronic pain.
Understanding the various conditions treated with anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents is vital not only for healthcare professionals but also for patients seeking relief. The effectiveness of these medications varies depending on individual circumstances and underlying health conditions, necessitating thorough medical evaluation and tailored treatment plans.
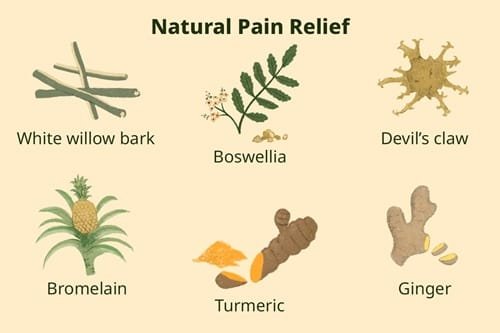
Natural Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Remedies
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in natural remedies for their anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. Many individuals seek alternatives to conventional medications due to concerns about side effects or long-term use. This section explores various herbs, supplements, and dietary choices that have demonstrated efficacy in alleviating inflammation and pain.
One of the most well-known anti-inflammatory herbs is turmeric, which contains curcumin, a compound praised for its potent anti-inflammatory effects. Research suggests that curcumin can inhibit various molecules involved in inflammation, making it a popular choice for those suffering from chronic inflammatory conditions such as arthritis. Similarly, ginger has been recognized for its analgesic properties, particularly in reducing muscle pain and soreness. Its beneficial effects can be attributed to its anti-inflammatory compounds, which help to mitigate pain responses in the body.
Another effective natural remedy is omega-3 fatty acids, predominantly found in fish oil. These fatty acids are noted for their ability to reduce inflammation and have been linked to decreased pain in conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis. Additionally, Boswellia serrata, commonly known as frankincense, has been shown in clinical studies to offer significant relief from inflammatory disorders and may be effective in improving mobility for those suffering from joint pain.
The diet also plays a crucial role in managing inflammation. Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can contribute to lower levels of inflammation. Foods such as berries, leafy greens, and fatty fish are particularly beneficial due to their high antioxidant content and anti-inflammatory properties. However, while these natural remedies can offer benefits, it is essential to consider potential risks such as allergies or interactions with prescribed medications, emphasizing the importance of consulting a healthcare professional before incorporating them into one’s routine.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
Anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents are widely utilized for their effective relief of pain and inflammation. However, their use is not without potential side effects and risks that merit close attention. Both short-term and long-term use of these medications can lead to various adverse effects, altering the safety profile of treatment and necessitating an informed approach by patients and healthcare providers alike.
One of the most common short-term side effects associated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is gastrointestinal discomfort, which can manifest as stomach pain, nausea, or even significant issues such as ulcers and gastrointestinal bleeding. These risks underscore the importance of following appropriate dosing guidelines and using protective agents when long-term treatment is considered.
Cardiovascular concerns also arise with the use of certain anti-inflammatory medications, particularly in individuals with pre-existing heart conditions. Long-term consumption of some NSAIDs has been linked to an elevated risk of heart attack and stroke, highlighting the critical need for medical supervision when using these drugs. Patients should engage in discussions with their healthcare providers regarding their cardiovascular health history before initiating treatment.
Furthermore, the analgesic landscape includes opioid medications, which, while effective for managing acute pain, carry a significant risk of dependency and addiction. Prolonged use of opioids can lead to tolerance, requiring higher doses for the same level of pain relief. This dependency can complicate treatment plans and result in difficulties when discontinuing use. Hence, healthcare practitioners advocate for opioid-sparing strategies whenever possible, employing alternatives and adjuvant therapies to minimize risks.
Consequently, a thorough understanding of these potential side effects and risks is essential in promoting the safe usage of anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents. By weighing the benefits against the associated dangers, patients can make informed choices tailored to their unique health circumstances.
The Future of Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Research
The realm of anti-inflammatory and analgesic research is witnessing a transformative era marked by continual advancements and novel approaches. Ongoing investigations aim to enhance the efficacy of existing medications while mitigating potential side effects. Central to this pursuit is the exploration of emerging therapies that leverage innovative compounds and biological mechanisms. Researchers are examining the potential of natural products, such as plant-based extracts, which have shown promise in delivering anti-inflammatory benefits with fewer adverse reactions compared to conventional pharmaceuticals.
Furthermore, advancements in drug formulations are paving the way for improved delivery systems. Nanotechnology is a significant focus area, facilitating targeted delivery of anti-inflammatory agents directly to the affected tissues. This targeted approach not only enhances the therapeutic outcomes but also minimizes systemic exposure, thereby reducing unwanted side effects. Such innovations are essential in addressing the challenges associated with traditional analgesics, which often carry risks of dependency and gastrointestinal complications.
The advent of personalized medicine represents another pivotal development in this field. By utilizing genetic profiling and advanced biomarkers, researchers aim to tailor anti-inflammatory and analgesic treatments to individual patient needs. This shift towards personalized approaches holds the potential to significantly improve treatment efficacy and patient adherence, as therapies can be aligned with the specific pathophysiological characteristics of each individual. Recent studies underscore the importance of understanding genetic variations in pain perception and inflammation responses, which can lead to the identification of more effective and safer treatment protocols.
As we look ahead, the intersection of technology, pharmacology, and genetics promises a future filled with innovative solutions. The dedicated efforts of researchers across disciplines not only inspire optimism regarding the management of pain and inflammation but also herald a new paradigm in healthcare that prioritizes patient-centered care. In conclusion, the ongoing research efforts in anti-inflammatory and analgesic treatments are set to transform clinical practices, fostering an era of more effective and personalized therapeutic options.
Conclusion: The Role of Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Agents in Health Care
Anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents are integral components of modern healthcare, widely utilized in managing pain and reducing inflammation. Their significance extends beyond mere symptom relief; they play a crucial role in enhancing the quality of life for individuals suffering from various medical conditions. From over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to prescription medications, these agents offer a range of therapeutic options tailored to address specific patient needs.
However, the effectiveness of these treatments must be balanced with an understanding of potential risks and side effects. Chronic use of NSAIDs can lead to gastrointestinal complications, cardiovascular issues, and kidney damage, making it essential for patients to utilize these medications judiciously. Furthermore, the propensity for misuse or reliance on stronger analgesics, such as opioids, necessitates careful monitoring by healthcare professionals. This underscores the importance of consulting with qualified practitioners when exploring anti-inflammatory and analgesic options. These professionals can provide guidance on appropriate dosages, duration of use, and alternative therapies that may complement pharmacological treatments.
A comprehensive approach to health care should also involve lifestyle changes and potential non-pharmacological interventions, such as physical therapy, dietary modifications, and mindfulness techniques. By integrating these strategies, patients can achieve better outcomes in managing both pain and inflammation. The dynamic nature of medicine necessitates ongoing research into the efficacy and safety of these agents, continuing to shed light on new applications and improved therapeutic strategies.
In conclusion, while anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents have proven invaluable in treating pain and inflammation, their optimal use is contingent upon informed decision-making and collaboration between patients and healthcare providers. This approach fosters a sustainable and effective management plan, enhancing overall health and wellness in the long term. If you like our posts about Supplements and Immunity Booster, Common Nutritional Deficiencies and Their Impact on Immunity, Key Supplements for Immunity Enhancement, Natural vs. Synthetic Supplements, and The Role of a Balanced Diet in Immune Health, etc, then follow us on Facebook, Instagram, X, and WhatsApp. Thank You.