Understanding the Orthopedic Range: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction to Orthopedics: Orthopedics is a specialized branch of medicine focused on the diagnosis, treatment, and management of musculoskeletal disorders. This field encompasses a wide range of conditions affecting bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, and muscles, which are essential for mobility and physical function. The significance of orthopedics lies in its ability to restore functionality and alleviate pain, which can drastically improve an individual’s quality of life.
There are two primary approaches within orthopedics: orthopedic surgery and non-surgical treatments. Orthopedic surgery involves invasive procedures to correct musculoskeletal issues, such as repairing broken bones, replacing damaged joints, or removing tumors. Conversely, non-surgical treatments may involve physical therapy, medication, or the use of braces and splints to manage conditions effectively without the need for surgery. Both approaches are crucial, and the choice between them often depends on the severity and nature of the patient’s condition.
Orthopedic conditions are increasingly prevalent across various populations, influenced by factors such as age, lifestyle, and general health. For instance, older adults often experience degenerative diseases like arthritis, while younger individuals may suffer from sports injuries. Moreover, sedentary lifestyles and obesity can exacerbate musculoskeletal issues, leading to a growing demand for orthopedic care.
Research indicates that an estimated one in two adults will experience a musculoskeletal condition at some point in their lives, underscoring the importance of understanding orthopedic principles. As awareness of these conditions increases, the role of orthopedics in providing effective treatment and enhancing overall health becomes even more critical.
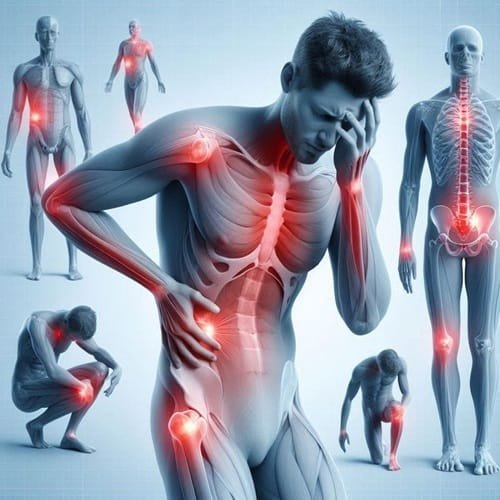
Common Orthopedic Conditions
Common Orthopedic Conditions: Orthopedic conditions encompass a broad range of issues affecting the musculoskeletal system. Among the most prevalent are arthritis, fractures, tendon injuries, and sports-related injuries. Each of these conditions presents distinct symptoms, causes, and demographic influences that contribute to their development.
Arthritis is one of the leading causes of pain and disability among adults, characterized by inflammation in the joints. The two most common types are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis typically occurs due to wear and tear on the joints over time, often influenced by age, obesity, or previous injuries. Symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. In contrast, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition that can affect individuals at any age, causing joint inflammation, pain, and fatigue.
Fractures, or broken bones, are another frequent orthopedic issue. They can result from accidents, falls, or high-impact activities, and they vary significantly in severity and healing time. Symptoms typically involve immediate pain, swelling, and an inability to use the affected limb. Demographic factors such as age play a crucial role; for instance, older adults may experience hip fractures more commonly due to factors like osteoporosis.
Additionally, tendon injuries, such as tendinitis or ruptures, often affect athletes and those engaging in repetitive motion activities. Tendinitis involves inflammation of a tendon, leading to pain and stiffness, particularly in the shoulders, elbows, and knees. Symptoms may include tenderness and a reduced range of motion. Sports-related injuries, which may encompass strains, sprains, and ligament tears, often arise during vigorous physical activity. These injuries can affect participants of all ages, particularly if proper techniques and precautions are not followed.
Understanding these common orthopedic conditions can guide individuals in recognizing symptoms that warrant professional evaluation and treatment. Early intervention is often key to effective management and recovery.
Diagnostic Techniques in Orthopedics
Diagnostic Techniques in Orthopedics: In the field of orthopedics, accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and patient recovery. Various diagnostic tools and techniques are employed by orthopedic professionals to gain a clear understanding of musculoskeletal conditions. The most commonly used methods include X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, each offering unique advantages in visualizing different aspects of the body.
X-rays are the most traditional and widely recognized imaging modality in orthopedics. They provide essential information about bone structure, alignment, and integrity. With the ability to reveal fractures, dislocations, and degenerative changes, X-rays serve as a foundational step in many orthopedic evaluations. The rapidity and cost-effectiveness of this technique make it an indispensable tool in the initial assessment of musculoskeletal issues.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) represents a significant advancement in diagnostic technology. Unlike X-rays, MRIs utilize powerful magnets and radio waves to produce detailed images of soft tissues, including cartilage, muscles, ligaments, and tendons. This capability makes MRI particularly valuable in diagnosing conditions such as tears, inflammation, and deteriorative diseases that may not be visible on X-rays. The precision and non-invasive nature of MRI scans allow orthopedic specialists to formulate comprehensive treatment plans based on the specific needs of their patients.
Computed Tomography (CT) scans offer yet another innovative imaging option. By combining X-ray technology with computer processing, CT scans generate cross-sectional images of the body, providing a more nuanced view than traditional X-rays. This technique is especially useful for complex fractures and joint issues, as it allows for better spatial visualization. Orthopedic professionals often rely on CT scans when facing intricate cases that require a more in-depth analysis.
In summary, the utilization of diagnostic techniques such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans has transformed orthopedic practice. These technologies empower healthcare providers to diagnose conditions accurately and develop tailored treatment strategies, reflecting the significant strides in orthopedic diagnostic capabilities. The ongoing evolution of these techniques continues to enhance the quality of patient care in orthopedic medicine.

Non-Surgical Treatment Options
In the field of orthopedics, non-surgical treatment options play a crucial role in managing a variety of conditions, including musculoskeletal disorders and injuries. These approaches not only help alleviate pain but also enhance mobility, allowing patients to maintain their daily activities without the need for invasive procedures.
One of the most common non-surgical treatment modalities is physical therapy. This involves a tailored program designed by a licensed physical therapist, focusing on exercises that strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected area, improve flexibility, and restore function. Physical therapy can also incorporate modalities such as ultrasound, electrical stimulation, and ice or heat application, which are effective in reducing pain and inflammation. The individualized approach ensures that the specific needs of each patient are addressed, making it an essential component of orthopedic care.
Medications are another vital aspect of non-surgical treatment options. Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with orthopedic conditions. In cases where pain persists, healthcare providers may prescribe stronger pain relievers or corticosteroids. Additionally, the incorporation of topical analgesics can provide localized pain relief without the systemic side effects of oral medications.
Another critical element of non-surgical treatments involves lifestyle modifications. These changes may include weight management, increased physical activity, and ergonomic adjustments to reduce strain on joints. Patients are often advised to engage in low-impact exercises, such as swimming, cycling, or yoga, which strengthen muscles without exacerbating existing conditions.
Together, these non-surgical treatment options form a comprehensive approach to managing orthopedic issues, making them integral to any treatment plan. Through physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle changes, patients can achieve pain relief and improved mobility, fostering a better quality of life.

Surgical Interventions in Orthopedics
Surgical interventions in orthopedics encompass a variety of procedures aimed at correcting musculoskeletal disorders, enhancing mobility, and alleviating pain. Among the most common types of surgical approaches are joint replacement, arthroscopy, and spinal surgery. These interventions are often considered when conservative treatment methods, such as physical therapy or medication, prove insufficient in providing relief or restoring function.
Joint replacement surgery, particularly of the hip and knee, is frequently performed for patients suffering from severe arthritis or joint degeneration. During this procedure, the damaged joint surfaces are removed and replaced with artificial implants. The decision to proceed with joint replacement typically involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s overall health, pain levels, and functional limitations, ensuring that the benefits of surgery outweigh the potential risks.
Arthroscopy, on the other hand, is a minimally invasive procedure used for diagnosing and treating joint issues. It involves the use of a small camera and instruments inserted through tiny incisions in the skin. This approach reduces recovery time and minimizes scarring compared to open surgery. Conditions such as torn cartilage, meniscus tears, and loose bodies can often be addressed using arthroscopy, resulting in improved joint function and a quicker return to daily activities.
Spinal surgery encompasses a range of procedures designed to address issues affecting the spinal column, including herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or deformities such as scoliosis. Surgeons use several techniques, including fusion or decompression, to relieve pressure on nerves and restore spine stability. The decision-making process for spinal surgery involves assessing the patient’s neurological function, pain severity, and specific spinal condition to formulate an appropriate treatment plan.
Potential risks associated with orthopedic surgeries include infection, blood clots, and anesthesia complications. While these procedures can offer substantial benefits, patients should engage in thorough discussions with their orthopedic surgeons to understand their risks and expected recovery timelines.

Rehabilitation in Orthopedics
The rehabilitation process following orthopedic treatments plays a crucial role in the recovery of patients. Orthopedic injuries and surgeries, which may include joint replacements, ligament repairs, or fracture fixations, often require a structured rehabilitation plan to ensure the best possible outcome. A comprehensive rehabilitation protocol focuses on restoring strength, improving range of motion, and facilitating the patient’s return to daily activities and sports.
Rehabilitation typically begins soon after the initial treatment. In many cases, patients may be encouraged to partake in gentle movements and exercises within days following surgery or injury, as this can significantly enhance the healing process. Early mobilization can help minimize stiffness and reduce muscle atrophy. As the healing progresses, the rehabilitation exercises will evolve in intensity and complexity, ensuring that patients gradually rebuild muscle strength and regain functionality.
Common rehabilitation exercises include stretching, strengthening, and balance training. These exercises are tailored to the individual’s specific needs, taking into consideration the type of orthopedic injury or procedure. Additionally, physiotherapists play a pivotal role in the rehabilitation process, assessing the patient’s progress and adjusting the exercise regimen as needed. Physiotherapists utilize a variety of modalities such as manual therapy and electrical stimulation to aid in recovery and pain management.
The timeline for recovery can vary based on several factors, including the type and severity of the orthopedic condition, the specific treatment received, and the patient’s overall health. Generally, a multi-phased approach is adopted, progressing from passive range of motion exercises to more vigorous activities as the patient heals. Active participation in the rehabilitation process is essential, as it empowers patients to take charge of their recovery, ultimately improving their outcomes. Proper adherence to rehabilitation protocols can significantly impact the overall success of orthopedic treatments.
Innovations and Trends in Orthopedic Care
The field of orthopedic care is undergoing remarkable transformations as a result of technological advancements and innovative practices. One of the standout developments is the rise of minimally invasive surgical techniques. Traditionally, orthopedic procedures required extensive incisions, leading to longer recovery times and increased post-operative pain. However, with the advent of minimally invasive approaches, surgeons can now perform complex operations through smaller incisions. This not only reduces trauma to the surrounding tissues but also enhances recovery speed, allowing patients to return to their normal activities more quickly.
Another noteworthy innovation in the orthopedic space is the incorporation of 3D printing technology for prosthetics. This innovation allows for the creation of custom-fitted implants and prosthetic devices tailored to the specific anatomical needs of each patient. By utilizing patient-specific imaging, orthopedic professionals can produce accurate and personalized replacements, leading to improved functionality and comfort for the user. Furthermore, the possibilities for rapid prototyping and creating trial prosthetics have the potential to significantly enhance pre-surgical planning and patient satisfaction.
Robotic assistance in orthopedic surgery is also a key trend reshaping the landscape of care. Robotic systems offer precise guidance during surgical procedures, resulting in improved accuracy and reduced complication rates. Surgeons can leverage these tools to perform intricate tasks with enhanced control, which is particularly beneficial in joint replacement surgeries. As robotic technology continues to evolve, it is anticipated that more orthopedic procedures will incorporate robotics, further solidifying its role in improving clinical outcomes.
In summary, the innovations in orthopedic care—ranging from minimally invasive procedures to advanced technologies like 3D printing and robotics—are significantly enhancing patient outcomes. As these trends continue to develop, they will undoubtedly shape the future of orthopedics, leading to safer, more effective treatment options for a diverse patient population.

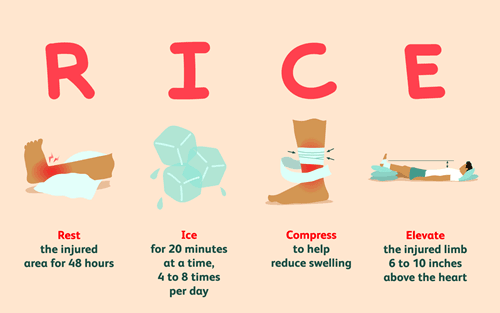
Self-Care and Prevention Strategies
Maintaining orthopedic health is crucial for overall well-being and can be achieved through effective self-care and prevention strategies. Incorporating regular exercise into daily routines is fundamental; this can include strength training, stretching, and aerobic activities that promote mobility and flexibility. Engaging in low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, can significantly reduce the risk of injury while also benefiting joint function. It is important to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise regimen, especially if one has existing orthopedic conditions.
Nutrition also plays a vital role in orthopedic health. A well-balanced diet that includes adequate levels of calcium and vitamin D supports bone strength, while anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fatty fish, may help manage pain and inflammation related to joint disorders. Staying hydrated is another essential component, as it aids in maintaining synovial fluid that lubricates the joints. Thus, prioritizing dietary choices can enhance overall orthopedic well-being and prevent potential issues.
Ergonomics should not be overlooked when considering strategies for preventing orthopedic injuries. Proper posture and ergonomic setups in both workplace and home environments can significantly reduce strain on muscles and joints. This includes using chairs with appropriate lumbar support, arranging workstations to promote neutral body positioning, and incorporating regular breaks to alleviate stress on specific body parts. Additionally, investing in supportive footwear can prevent injuries related to higher-impact activities like running or standing for extended periods.
By integrating these strategies—regular exercise, a balanced diet, and proper ergonomic practices—individuals can proactively support their orthopedic health. Managing existing conditions while taking preventative measures can empower individuals to take an active role in their orthopedic well-being and enhance their quality of life.
Conclusion and Resources:
Understanding the orthopedic range is vital for anyone navigating the complexities of musculoskeletal health. From the basic anatomy of bones and joints to the latest advancements in treatment options, gaining insight into orthopedic care enhances our ability to address injuries and chronic conditions effectively. This knowledge empowers patients and caregivers alike to make informed decisions regarding treatment pathways and rehabilitation processes.
Orthopedic conditions can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, leading to pain, limited mobility, or even disability. By familiarizing oneself with common orthopedic issues such as arthritis, fractures, and sports injuries, patients can better advocate for their health needs. Furthermore, understanding the various treatment methods, including physical therapy, surgical options, and alternative therapies, fosters a collaborative approach between patients and healthcare professionals.
For those seeking further knowledge, a wealth of resources is available. The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) offers educational materials and guidance on a range of orthopedic conditions and treatments. Websites such as MedlinePlus provide reliable health information, while the National Institutes of Health (NIH) features ongoing research that can shed light on emerging therapies and preventive measures.
Additionally, joining support groups or forums can be invaluable for individuals facing orthopedic challenges. Engaging with those who share similar experiences can offer emotional support, practical advice, and insights into effective coping strategies. Printed literature, such as “The Orthopedic Handbook,” can also serve as a comprehensive guide for both patients and healthcare providers.
In conclusion, understanding orthopedic care is essential for managing musculoskeletal health effectively. By utilizing the resources available and remaining informed, individuals can navigate their treatment options more confidently, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes.
If you like our posts about GOrthopedic Range, Common Orthopedic Conditions, Diagnostic Techniques in Orthopedics, Non-Surgical Treatment Options, Surgical Interventions in Orthopedics, etc, then follow us on Facebook, Instagram, X, and WhatsApp. Thank You.
Read More: Introduction to Anti-Infective Agents


